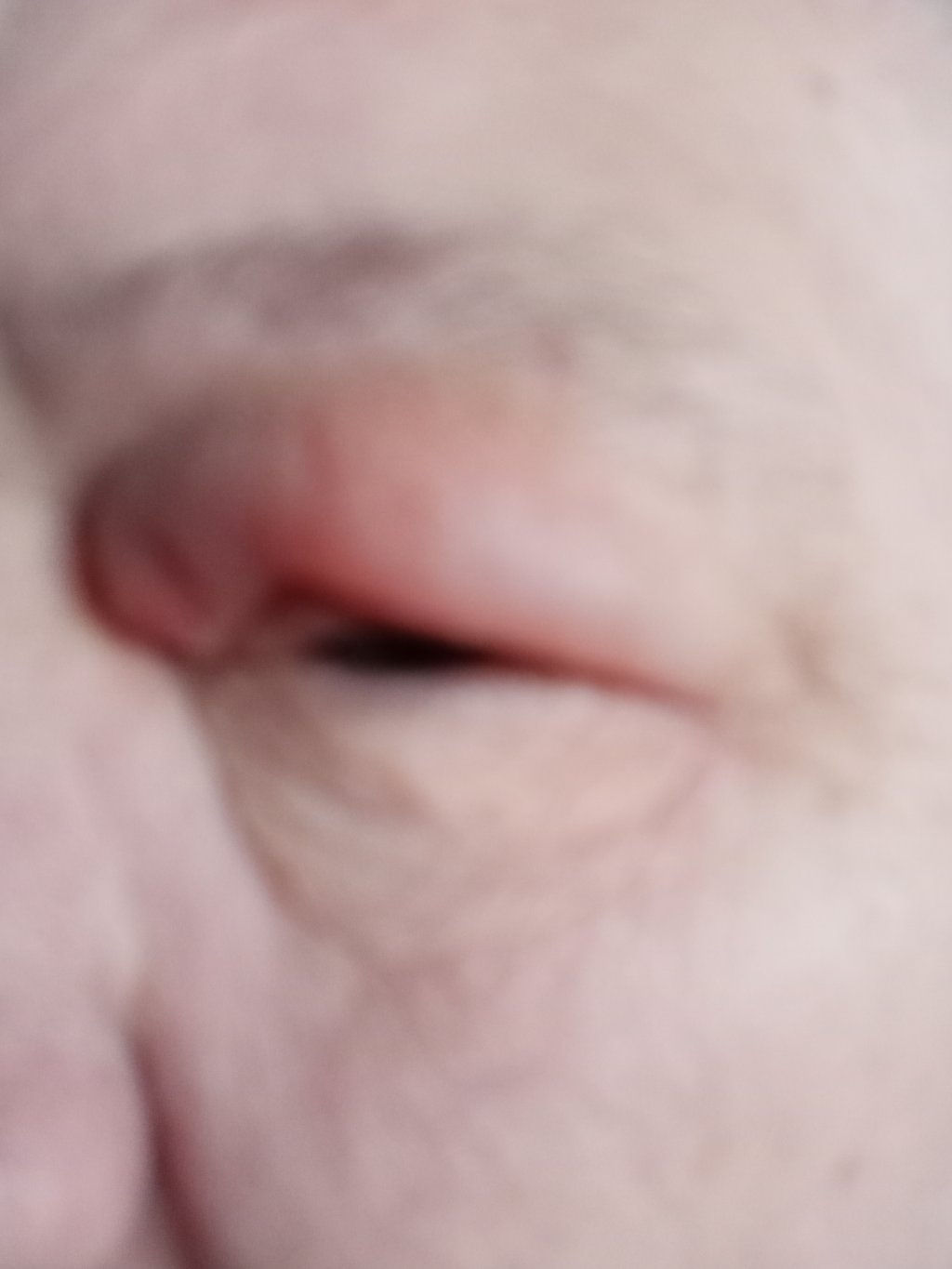
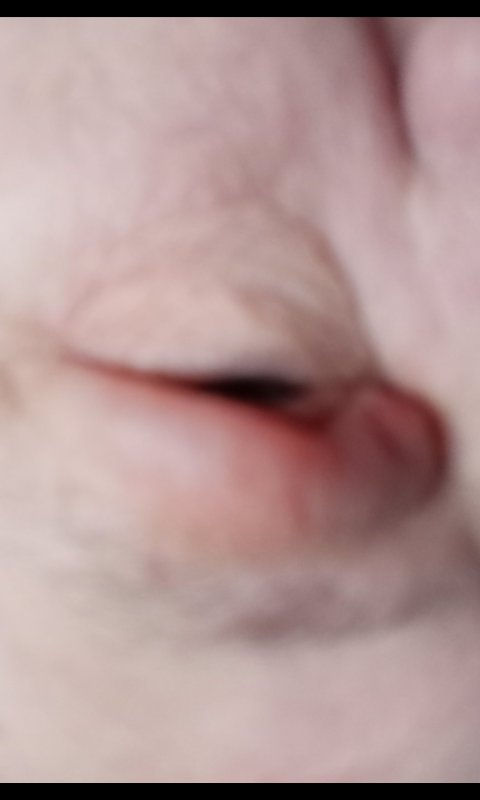
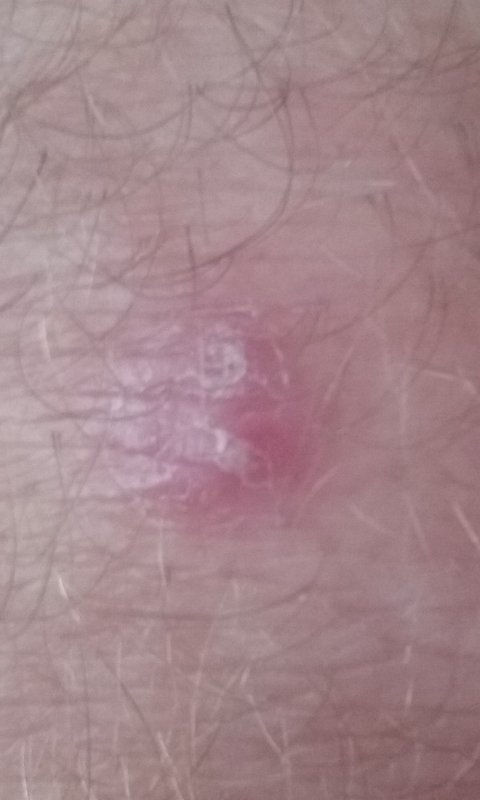
Red-Back spiders - highly venomous - can be deadly
Area of distribution: Australia-wide.
Venom toxicity: The Red-Back spider can inflict a painful bite which can be fatal, especially to the young and elderly. An effective anti-venom was developed in 1956. About 250 people receive the anti-venom each year.
Nerve poison: Only a small amount of venom can cause serious illness, as the poison attacks the nervous system. Systemic envenomisation usually results in headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia, hypertension and in severe cases, paralysis.
Excruciating pain: The pain around the spider bite area can be excruciating. If bitten, immediately apply first aid and seek medical attention (ambulance) should be sought as soon as possible.
Spider Identification: -The red-back spider size varies greatly. The male can be tiny, with the abdomen of the female growing to the size of a large pea. Red-back spiders do NOT always have a "red" marking.
Habitat: The red-back spider prefers dry habitats; is often found in out-houses, letter-boxes, underside of seats, in rubbish, such as empty cans, in the sub-floor and other dark areas. Electric lights attract their prey, such as moths, flies, mosquitoes and other insects.
FIRST AID...for Red-Back & Other Spider Bites
As the venom of the red-back and other spiders moves very slowly, any attempt to restrict its progress would only serve to increase the associated pain, which can be excruciating. Do not bandage (except for funnel-web spider bite - see above).
The patient should be kept calm and reassured; all undue movement should be avoided.
Use an ice-pack on the bite site to reduce the swelling.
Medical First Aid should be sought immediately. Many hospitals and ambulance vehicles carry the Red-back anti-venom. If safe to do so, take the spider to the hospital for identification.
Symptoms of Venomous Spider Bites
The fangs of a Red-Back Spider are tiny and it's bite may often go unnoticed, but, often a sharp pin-prick may be felt. This is generally followed by severe pain at the site of the bite, leading to more general pain.
Other symptoms of venomous spider bites include headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, abdominal pain, and partial loss of muscle control.
Sweating occurs in varying degrees, particularly around site of the bite.
Swelling of the affected area is common, as is a quickening of the heart-beat.
Hope it all ends well for you goody, sounds like a red back bite, been bitten a few times and your
symptoms similar to mine. all the best.